Conclusion
In conclusion, the Quaker Salmonella case serves as a catalyst for a broader conversation about food safety and the ongoing challenges we face in preventing foodborne illnesses. By understanding that Salmonella is not confined to eggs alone, we can take a more comprehensive approach to food safety that encompasses all types of food products. This understanding empowers us to make informed choices, adopt safer food handling practices, and advocate for stronger food safety regulations.
As consumers, we have a responsibility to stay informed and vigilant. The Quaker incident is a reminder that food safety is not just the responsibility of producers and regulators; it is a shared responsibility that requires active participation from everyone. By being aware of the risks, staying informed about recalls, and practicing good hygiene, we can help protect ourselves and our families from the dangers of foodborne illnesses.
Moving forward, it is crucial that we continue to educate ourselves about food safety and support efforts to improve food safety standards. The lessons learned from the Quaker incident should not be forgotten, but rather used as a stepping stone toward a safer and healthier food supply for all.
FAQs
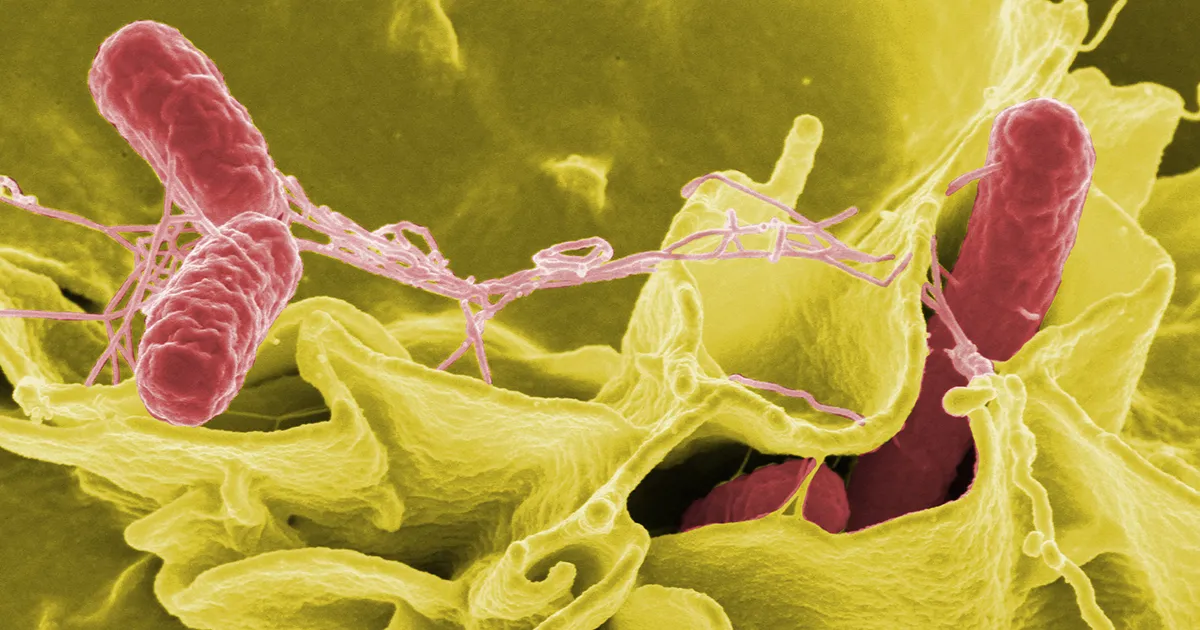
1. What is Salmonella and how does it affect health? Salmonella is a type of bacteria that can cause food poisoning, leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. It can be particularly dangerous for young children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems.
2. How did Salmonella contamination occur in Quaker products? While the specific details of how Salmonella entered Quaker products are not fully disclosed, contamination can occur at various stages of production, from raw material sourcing to processing and packaging. This incident underscores the need for rigorous quality control in the food industry.
3. Is Salmonella only found in eggs and poultry? No, Salmonella can contaminate a wide range of food products, including cereals, fruits, vegetables, and processed foods. It is important to recognize that Salmonella is not limited to any one type of food.
4. What steps can consumers take to reduce the risk of Salmonella infection? Consumers can reduce the risk by thoroughly washing fruits and vegetables, cooking food to the proper temperature, avoiding cross-contamination in the kitchen, and staying informed about food recalls.
5. What should I do if I have purchased a product that is recalled due to Salmonella contamination? If you have purchased a product that is recalled, do not consume it. Follow the instructions provided by the recall notice, which may include returning the product to the store or disposing of it safely.






