The Impact of Chronic Stress on Aging
The Stress Epidemic in Generation Z
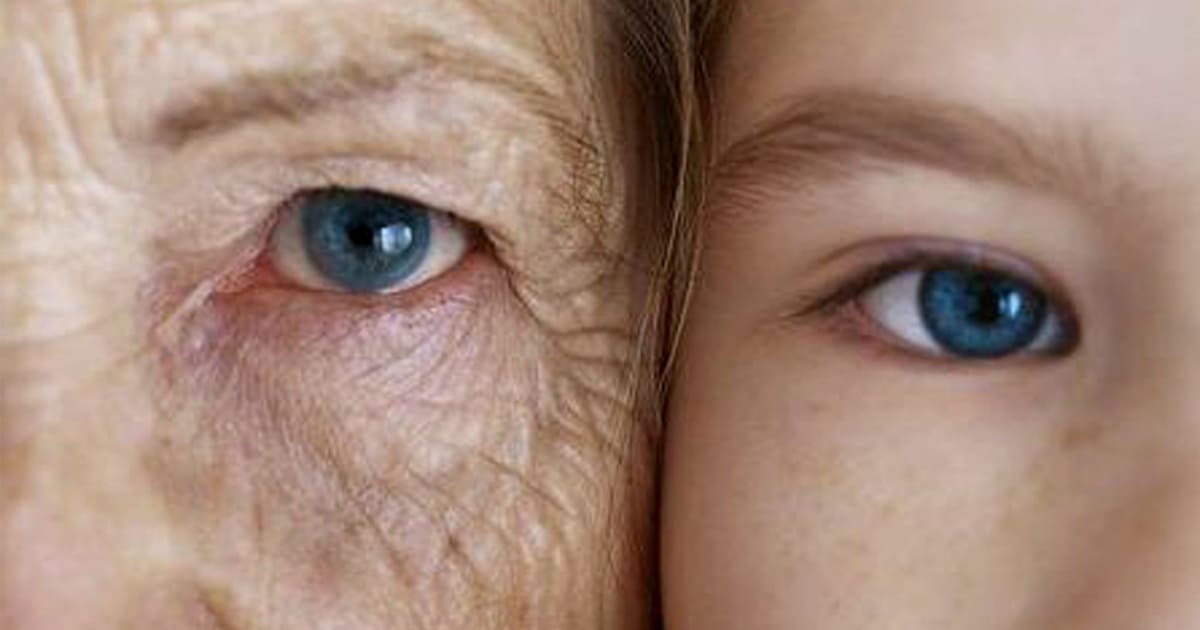
Generation Z faces unique challenges that previous generations did not, including the pressures of navigating a complex digital landscape and meeting high expectations in various aspects of life. This constant pressure has led to heightened stress levels, which can have serious implications for overall health. Chronic stress is known to impact the body’s physiological systems, leading to premature aging signs such as wrinkles, decreased skin elasticity, and weakened immune function.
How Stress Accelerates Aging
Chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that, in excess, can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress. These processes are linked to cellular aging and can accelerate the visible signs of aging. Moreover, stress can disrupt sleep patterns, further exacerbating its negative effects on physical health. Addressing stress through mindfulness practices, therapy, and stress management techniques is essential for mitigating its impact on aging.
The Role of Fast Food in Premature Aging
The Prevalence of Unhealthy Eating Habits
Fast food has become a staple for many in Generation Z due to its convenience and affordability. However, the reliance on processed and unhealthy foods can significantly impact health and contribute to premature aging. Fast food is typically high in refined sugars, saturated fats, and additives, all of which can lead to inflammation and oxidative damage in the body.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Aging
A diet high in fast food often lacks essential nutrients that are crucial for maintaining healthy skin, optimal energy levels, and overall well-being. Nutritional deficiencies can accelerate the aging process by impairing cellular function and reducing the body’s ability to repair itself. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help counteract the effects of unhealthy eating habits.
The Impact of Sedentary Lifestyles on Health
Decreased Physical Activity Among Youth
The rise of digital technology has led to an increase in sedentary behavior among Generation Z. Extended hours spent on electronic devices and a decrease in physical activity contribute to a sedentary lifestyle. Regular exercise is vital for maintaining cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and metabolic function, all of which play a role in slowing the aging process.
Benefits of Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity helps to manage stress, improve mood, and support overall health. Exercise promotes better sleep, boosts energy levels, and enhances cognitive function. Incorporating physical activity into daily routines can help mitigate the effects of a sedentary lifestyle and promote healthier aging. Activities such as walking, jogging, yoga, and strength training are beneficial for maintaining youthful vitality.
Strategies for Combating Premature Aging
Stress Management Techniques
Implementing effective stress management strategies is crucial for mitigating its impact on aging. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help reduce stress levels. Additionally, seeking support from mental health professionals and engaging in relaxing hobbies can contribute to overall well-being.
Adopting a Balanced Diet
Transitioning to a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for combating premature aging. Focus on incorporating whole, unprocessed foods into your diet, including a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Reducing the consumption of fast food and sugary snacks can help prevent inflammation and support overall health.
Promoting an Active Lifestyle
Encouraging regular physical activity is vital for maintaining health and slowing the aging process. Find activities that you enjoy and make them a part of your daily routine. Whether it’s a structured workout, recreational sports, or simply walking more, staying active is key to promoting long-term health and well-being.